Part 1 - Artificial intelligence in Internal Audit: How to create a RACM using building blocks
Welcome to my mini-series on how to use Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Internal Audit. These examples are specifically for the free version of ChatGPT and Microsoft Copilot. Stay tuned for useful tips to save you time, just like having an intern, they can help you build a strong draft that might be 80% of the way there and will still require your detailed review.
Introduction: Tips for prompting
1. Complete prompts in one session before a time out to avoid losing the session content you build (only applicable if you use the trial version of Microsoft Copilot or are not signed into a ChatGPT account)
2. Always fact-check the content produced, which can make errors and create false data.
3. Ask Copilot or ChatGPT to change your content to UK English.
4. Export and SAVE an offline copy of your prompts and outputs as you go.
5. You can copy and paste in tables with data for quick data analytics (if you are unable to upload files, specific to free versions)
6. Execute prompts to sense check / perform a gap analysis of your work e.g.
What are the key risks for XYZ?
What are the key risks to complying with XYZ standards?
What are the key risks from a Chief Risk Officer Perspective? Etc.
7. If you want a certain number of options provided, specify a specific number. E.g., Produce 10 more options.
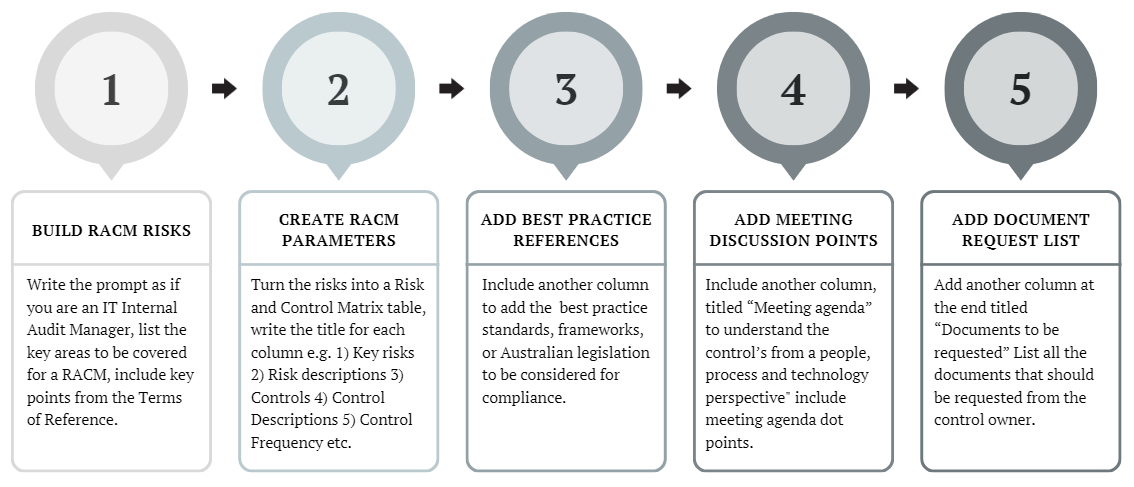
How to use five building blocks to create a Risk and Control Matrix (RACM)
Building Block 1 - Build a list of tailored risks
Example prompt – Create the risks: Who, where, what, how, and specific requirements
“Assuming you are an IT internal Audit Manager for an insurance company, what are the key areas to be considered for a RACM when implementing Microsoft Copilot, make sure the AI risks include, large language models vulnerabilities, web application firewalls, prompt injections, web application firewalls best practices, filtering model inputs, and no attempts for jailbreak, model abuse, data sensitisation, monitoring anomaly behaviours.”
Building Block 2: Create the RACM parameters
Example prompt – Create table and headers
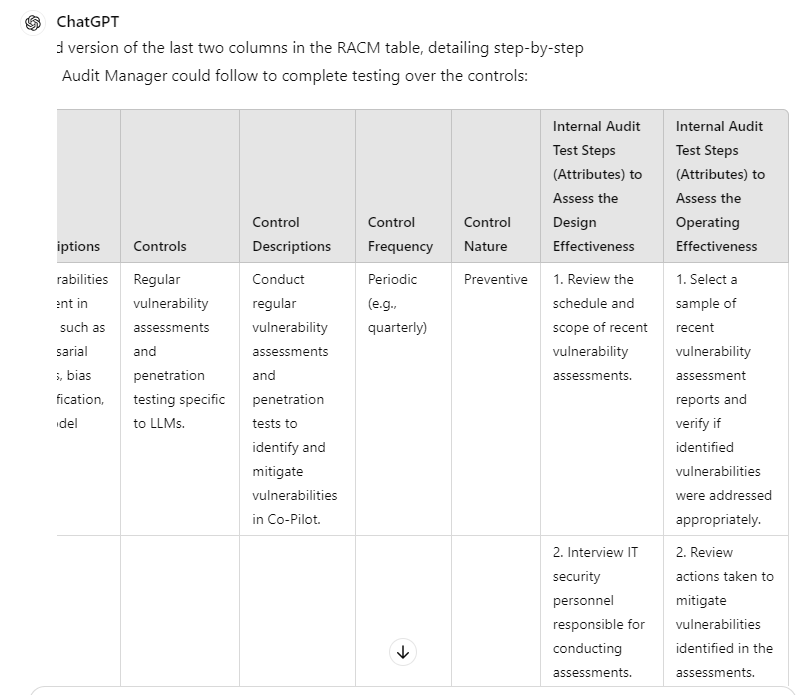
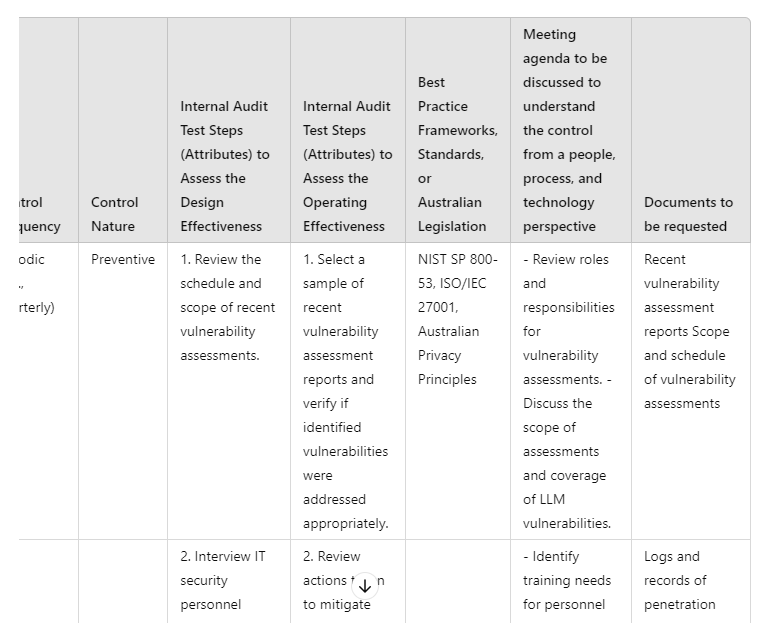
“Turn the above into a Risk and Control Matrix table, make the columns into the following layout 1) Key risks 2) Risk descriptions 3) Controls 4) Control Descriptions 5) Control Frequency 6) Control Nature 7) Internal Audit test steps (attributes) to assess the design effectiveness 8) Internal Audit test steps (attributes) to assess the operating effectiveness”
Example prompt – Detailed test steps
“Update the last two columns to include step-by-step instructions that could be completed by the Internal Audit Manager to complete testing over the controls, list each test attribute include, interview the stakeholders, request the appropriate files and review specific elements to mitigate the risks.”
Building Block 3: Add best practice references
Example prompt – References URLs
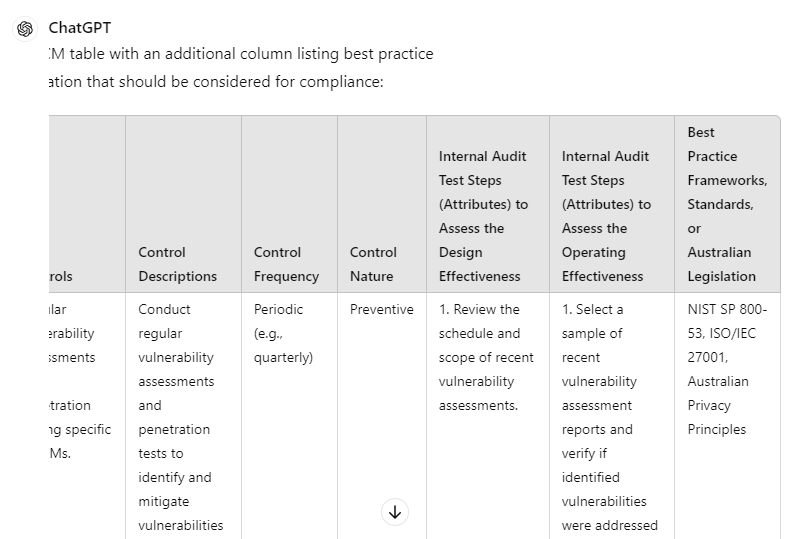
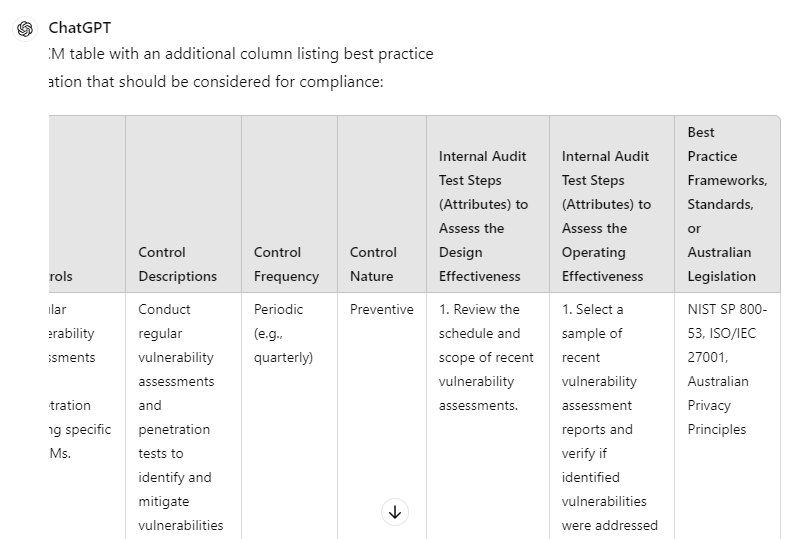
“Include another column with best practice frameworks, standards, or Australian legislation to be considered for compliance”
Building Block 4: Add meeting agendas
Example prompt update – Meeting Agendas
“Include another column at the end, called "Meeting agenda to be discussed to understand the control from a people, process and technology perspective" include dot points for the meeting agendas”
Building Block 5: Add a document request list
Example prompt update – Documents to request
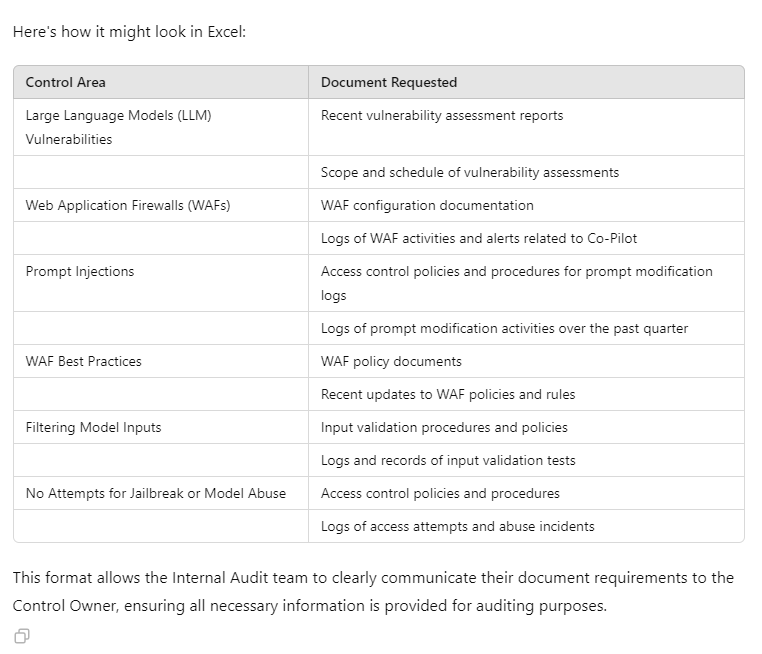
“Add another column at the end titled) Documents to be requested. List all the documents that should be requested from the control owner”
Example prompt update – Document Request
Based on the above, create another table designed as Document Request in Microsoft Excel, this request will be sent from Internal Audit to the Control Owner.
Free AI courses
• Microsoft - AI For Beginners Curriculum https://lnkd.in/efYVSKQk
• Introduction to Artificial Intelligence https://lnkd.in/euByJFBk
• What Is Generative AI? https://lnkd.in/eJp9hBET
• Generative AI: The Evolution of Thoughtful Online Search https://lnkd.in/eKAvkN4Y
• Ethics in the Age of Generative AI https://lnkd.in/eTA6SeKq
• AI Essentials - lnkd.in/dyEt4DGt
• ChatGPT Mastery - lnkd.in/eiRtk-6q
• Google AI Magic - lnkd.in/eBQXfBe9
• Harvard AI Introduction - lnkd.in/eu4mZaAG
• Microsoft AI Basics - lnkd.in/eYNWzXUX
• Prompt Engineering Pro - lnkd.in/eNi_YNSe
• Google's Ethical AI - lnkd.in/eTrwSU89
• Machine Learning by Harvard - lnkd.in/eX28syMJ
• Language Models by LangChain - lnkd.in/evZVJbNy
• Generative AI by Microsoft - lnkd.in/dqjnzcCD
• Amazon's AI Strategy - lnkd.in/dFhmsvZC
• AWS AI Foundations - lnkd.in/dEjN9PRm